- Best First Search Algorithm(Greedy search)
Best-first Search Algorithm (Greedy Search):
Greedy best-first search algorithm always selects the path which appears best at that moment. It is the combination of depth-first search and breadth-first search algorithms. It uses the heuristic function and search. Best-first search allows us to take the advantages of both algorithms. With the help of best-first search, at each step, we can choose the most promising node. In the best first search algorithm, we expand the node which is closest to the goal node and the closest cost is estimated by heuristic function, i.e.
Were, h(n)= estimated cost from node n to the goal.
The greedy best first algorithm is implemented by the priority queue.
Best first search algorithm:
- Step 1: Place the starting node into the OPEN list.
- Step 2: If the OPEN list is empty, Stop and return failure.
- Step 3: Remove the node n, from the OPEN list which has the lowest value of h(n), and places it in the CLOSED list.
- Step 4: Expand the node n, and generate the successors of node n.
- Step 5: Check each successor of node n, and find whether any node is a goal node or not. If any successor node is goal node, then return success and terminate the search, else proceed to Step 6.
- Step 6: For each successor node, algorithm checks for evaluation function f(n), and then check if the node has been in either OPEN or CLOSED list. If the node has not been in both list, then add it to the OPEN list.
- Step 7: Return to Step 2.
Advantages:
- Best first search can switch between BFS and DFS by gaining the advantages of both the algorithms.
- This algorithm is more efficient than BFS and DFS algorithms.
Disadvantages:
- It can behave as an unguided depth-first search in the worst case scenario.
- It can get stuck in a loop as DFS.
- This algorithm is not optimal.
Example:
Consider the below search problem, and we will traverse it using greedy best-first search. At each iteration, each node is expanded using evaluation function f(n)=h(n) , which is given in the below table.
In this search example, we are using two lists which are OPEN and CLOSED Lists. Following are the iteration for traversing the above example.
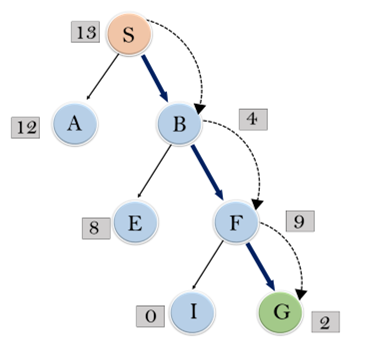
Expand the nodes of S and put in the CLOSED list
Initialization: Open [A, B], Closed [S]
Iteration 1: Open [A], Closed [S, B]
Iteration 2: Open [E, F, A], Closed [S, B]
: Open [E, A], Closed [S, B, F]
Iteration 3: Open [I, G, E, A], Closed [S, B, F]
: Open [I, E, A], Closed [S, B, F, G]
Hence the final solution path will be: S----> B----->F----> G
Time Complexity: The worst case time complexity of Greedy best first search is O(bm).
Space Complexity: The worst case space complexity of Greedy best first search is O(bm). Where, m is the maximum depth of the search space.
Complete: Greedy best-first search is also incomplete, even if the given state space is finite.
Optimal: Greedy best first search algorithm is not optimal.